What is hyperglycemia? It is the medical term for high blood sugar. It’s a condition in which the blood plasma has too much glucose. Glucose is found in most foods and is used by the body to supply energy to cells. In a healthy person, insulin is released from the pancreas and used to help the cells convert glucose into energy. It is caused when the body does not have enough insulin or can’t properly use the insulin it produces. As a result, the body is unable to break down the blood glucose for energy. Chronic hyperglycemia that remains at consistently high levels is known as diabetes mellitus.
Temporary Hyperglycemia
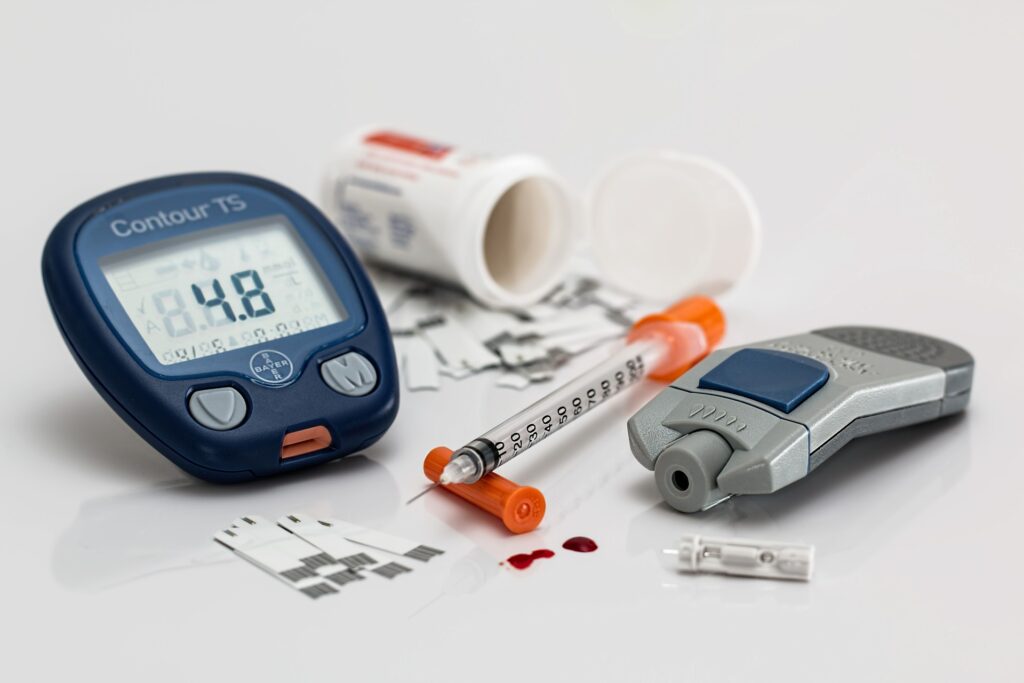 The amount of sugar in a person’s blood plasma can change before and after meals and throughout the day. Temporary hyperglycemia can be caused by eating more or exercising less than planned. Smoking can cause an increase in the amount of glucose in the blood. It can result from stress due to an illness, like a cold or flu, or due to life events. It can even be caused by eating too many carbohydrates or occur after strenuous physical activity. While this kind of temporary, infrequent hyperglycemia is not a cause for concern, temporary acute hyperglycemia can be more serious.
The amount of sugar in a person’s blood plasma can change before and after meals and throughout the day. Temporary hyperglycemia can be caused by eating more or exercising less than planned. Smoking can cause an increase in the amount of glucose in the blood. It can result from stress due to an illness, like a cold or flu, or due to life events. It can even be caused by eating too many carbohydrates or occur after strenuous physical activity. While this kind of temporary, infrequent hyperglycemia is not a cause for concern, temporary acute hyperglycemia can be more serious.
The risk of temporary acute hyperglycemia is increased by certain drugs. In the absence of diabetes, acute stress, such as a stroke or a myocardial infarction, can cause it. It can also be caused by thyroid, pituitary, or adrenal gland dysfunctions, diseases of the pancreas, or certain kind of infections. Certain types of physical trauma can also increase blood levels, though rarely for more than a brief time or to very high levels. Acute episodes of hyperglycemia without these obvious causes may indicate pre-diabetes or a genetic predisposition to diabetes.
Chronic Hyperglycemia
Chronic hyperglycemia, or a consistently high level of blood glucose, is the defining marker of diabetes. Classic symptoms of chronic hyperglycemia include frequent hunger, thirst, or urination. Symptoms can also include fatigue, dry mouth, weight loss, blurred vision, headaches, and difficulty concentrating. Hyperglycemia and diabetes can have serious, life-threatening complications. Damage to nerves, body organs, and blood vessels can occur, and more serious medical conditions can follow.
Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis is a condition caused by chronic hyperglycemia. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, very dry mouth, and shortness of breath. It requires immediate treatment. Chronic hyperglycemia can cause heart injuries and is frequently associated with heart attacks and death, even in patients with no history of heart disease.
Treatment
While oral medications or insulin treatment may be prescribed for diabetes, the first and most powerful method of treatment for chronic hyperglycemia or diabetes generally involves lifestyle changes. Losing weight and increasing physical activity both help the body to become more sensitive to insulin, in turn helping it to control the levels of glucose in the blood. A diabetic diet, a balanced diet that is low in cholesterol, fat, and sugar, but high in fiber, with calories spread evenly throughout the day, has also been shown to help reduce the incidence of hyperglycemia. Because smoking has been shown to raise blood sugar levels, quitting smoking also assists in the treatment of hyperglycemia.

Good information to pass along to my pre-diabetic mom!